TM 5-6115-400-35
Figure 124. Simplified schematic diagram of voltage regulator.
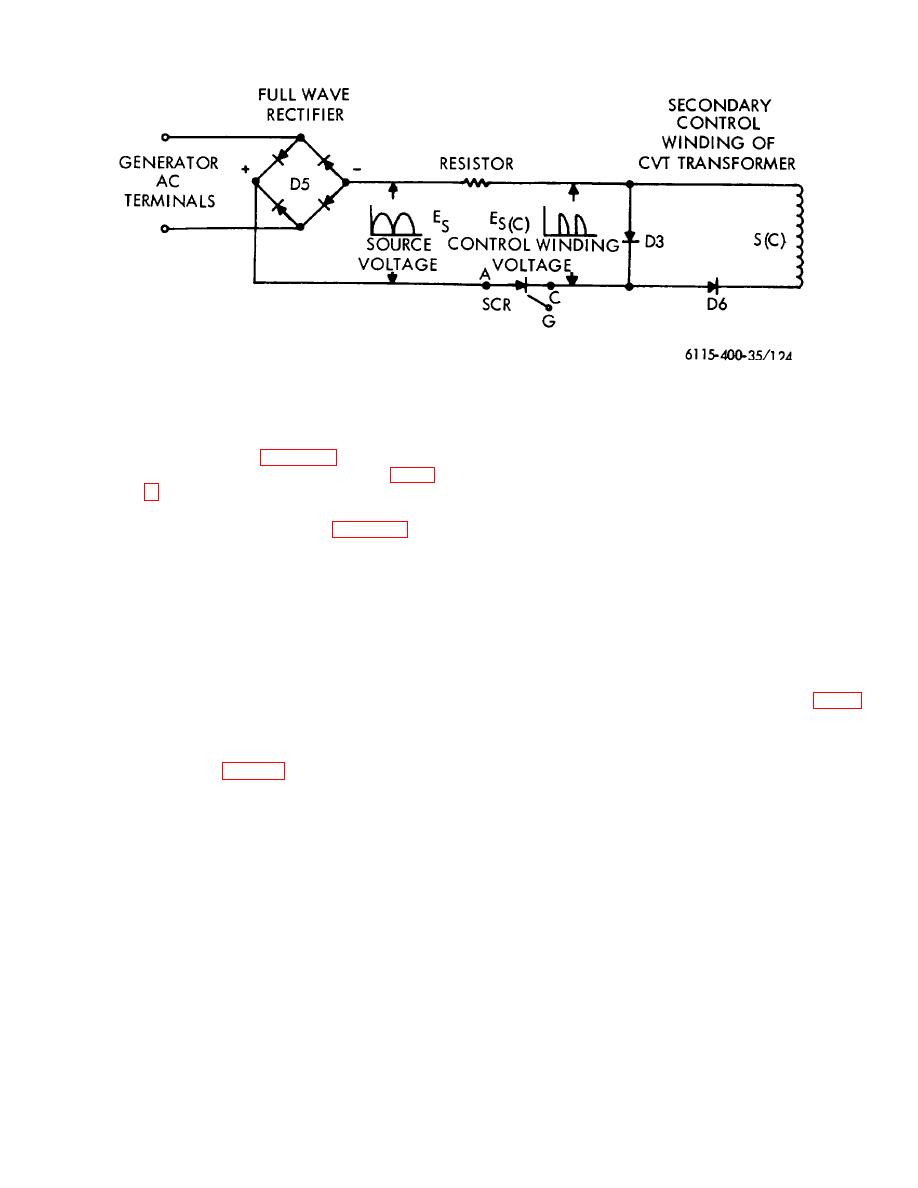
CVT. The SCR regains the ability to
limits for the various load conditions to be
absorb voltage when the source voltage
encountered. The basic elements of the
drops to zero at the end of each cycle of
voltage regulator are illustrated in block
pulsating dc (1/120 second based on a 60
diagram form in figure 118 and explained
cps ac input to D2). Thus; by applying a
in the following paragraphs, refer to figure
voltage pulse between points G and C
each cycle, and shifting the pulse in time
(3) The control current supplied the S (C)
with respect to the cycle, full control of the
winding of the CVT (fig.
120) is
control current applied to the S (C)
developed by the full-wave rectifier D5
winding is established.
which received a portion of the generator
(4) The pulse control circuit which supplies
output. The amount of control current
the voltage pulse to the silicon controlled
supplied is determined by the silicon
rectifier (SCR) consists of a unijunction
controlled rectifier SCR (power amplifier
semi-conductor (Q2) and resistors R6 and
of fig.124). Isolation transformer T3 at
R7. The action of this circuit is such that
this point isolates the circuit that contains
when the voltage level between the
silicon controlled rectifier SCR from the
emitter and Number 1 base of the
main lines, preventing feed-back and
unijunction semiconductor (see fig. 1)
eliminating radio interference. The silicon
reaches approximately 10 volts, the Q2
controlled
rectifier
possesses
triggers. This allows the energy stored in
characteristics that enable it to absorb all
capacitor C2 to discharge through resistor
the source voltage E. between points A
R7, triggering the silicon controlled
and C (see fig. 124) until such time as a
rectifier.
voltage pulse is applied between points G
and C. At the instant the voltage pulse is
(5) A phase shifting network consisting of
applied, the SCR can no longer absorb
transistor Q1, resistor R4 and capacitor
voltage, the voltage across A and C drops
C2, is used to determine at what point of a
to zero, and the source voltage E, ap 158
given cycle the unijunction semiconductor
pears across the S (C) winding of the
will fire.
158


